1. Conservative (Non-Surgical) Treatment
- Dietary changes: Increase fiber and fluids to keep stools soft.
- Sitz baths: Sitting in warm water helps relax the muscles and relieve pain.
- Topical ointments: Use only topical ointments.
- Laxatives: Help prevent constipation and reduce straining.
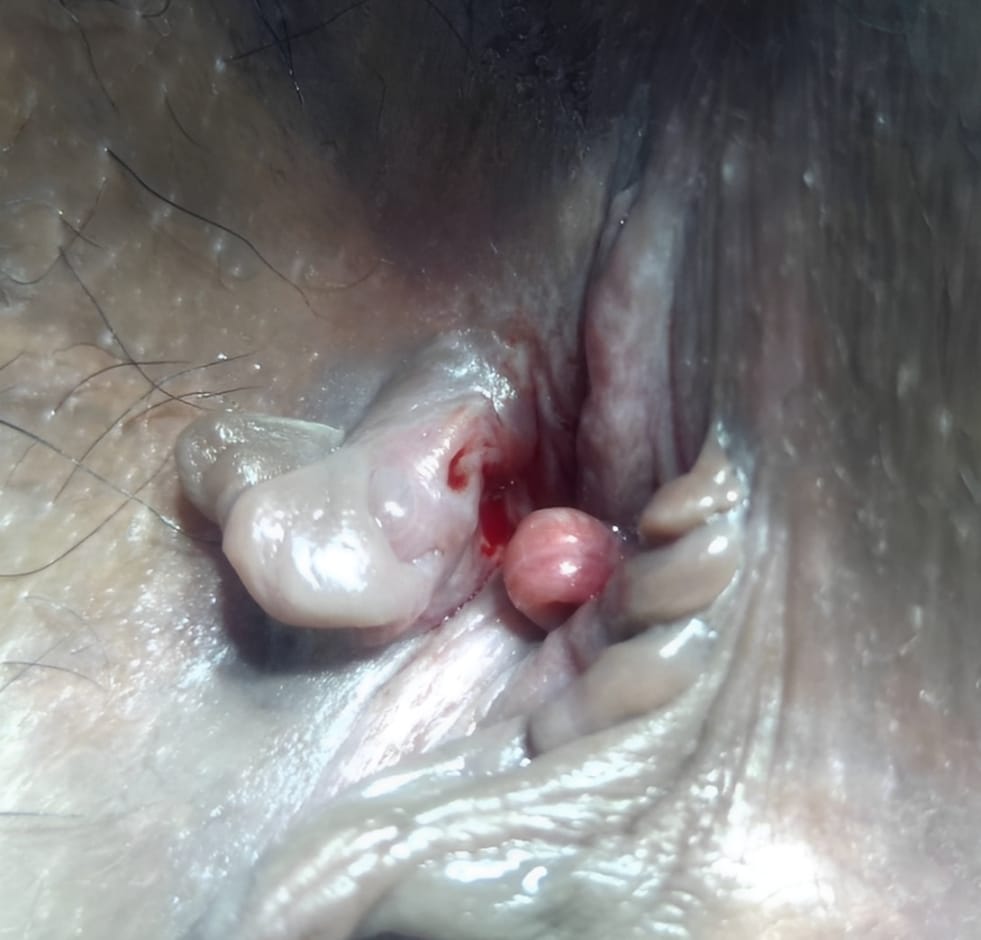
2. Surgical Treatment
If non-surgical methods fail (especially for chronic fissures), surgery may be recommended.
- Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy (LIS): The gold standard. A small cut is made in the internal sphincter muscle to reduce spasms and promote healing. This can be done using a traditional scalpel, electrocautery, or a laser.